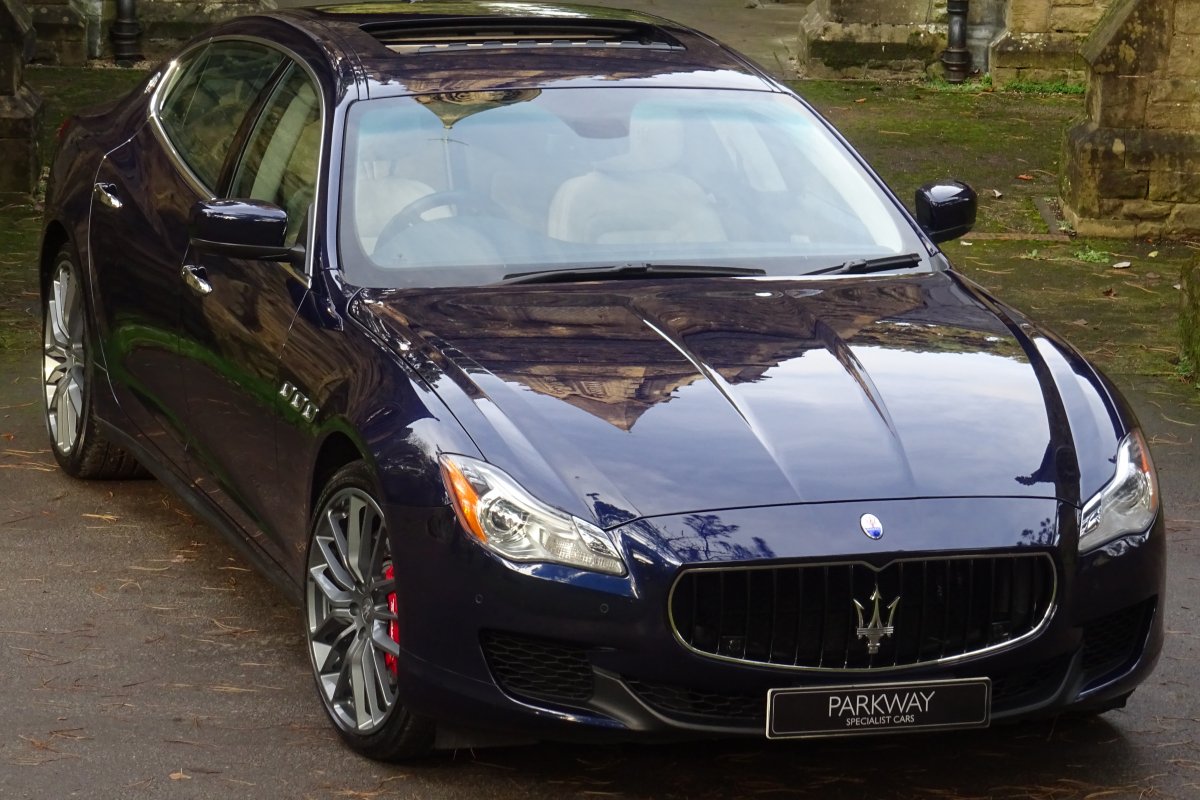
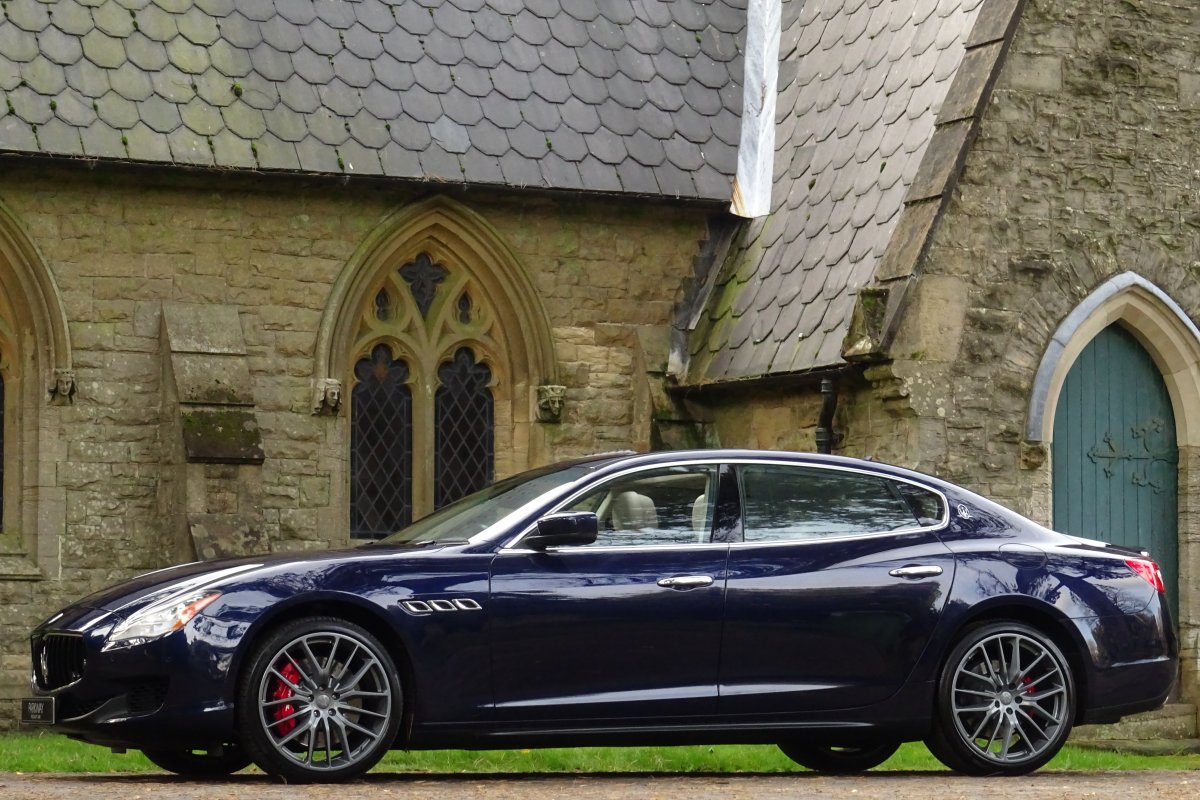
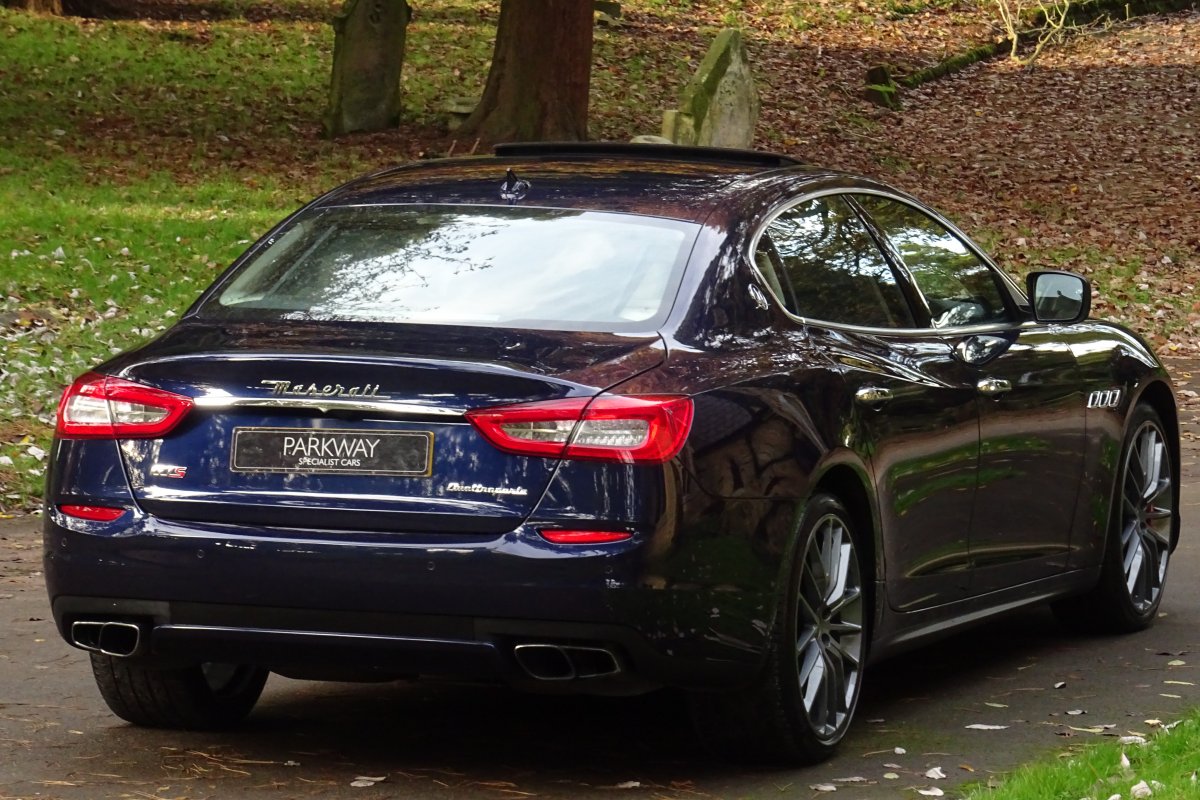
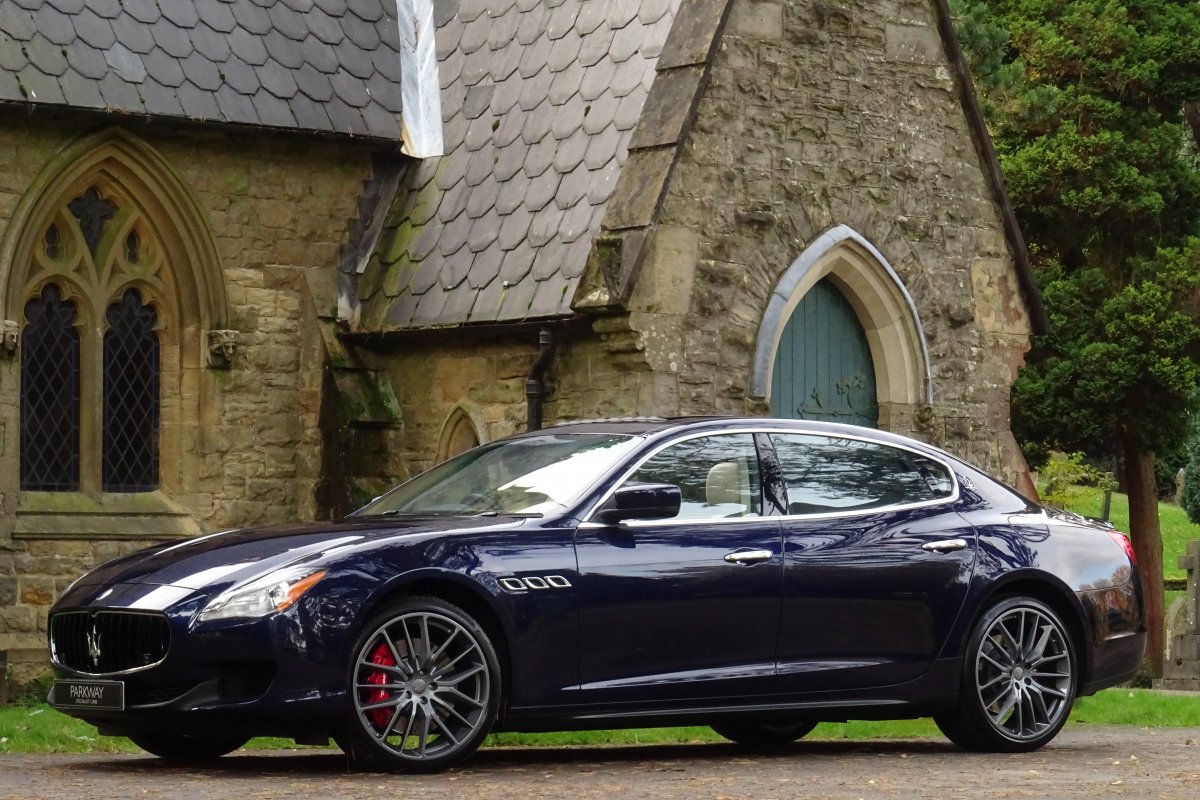
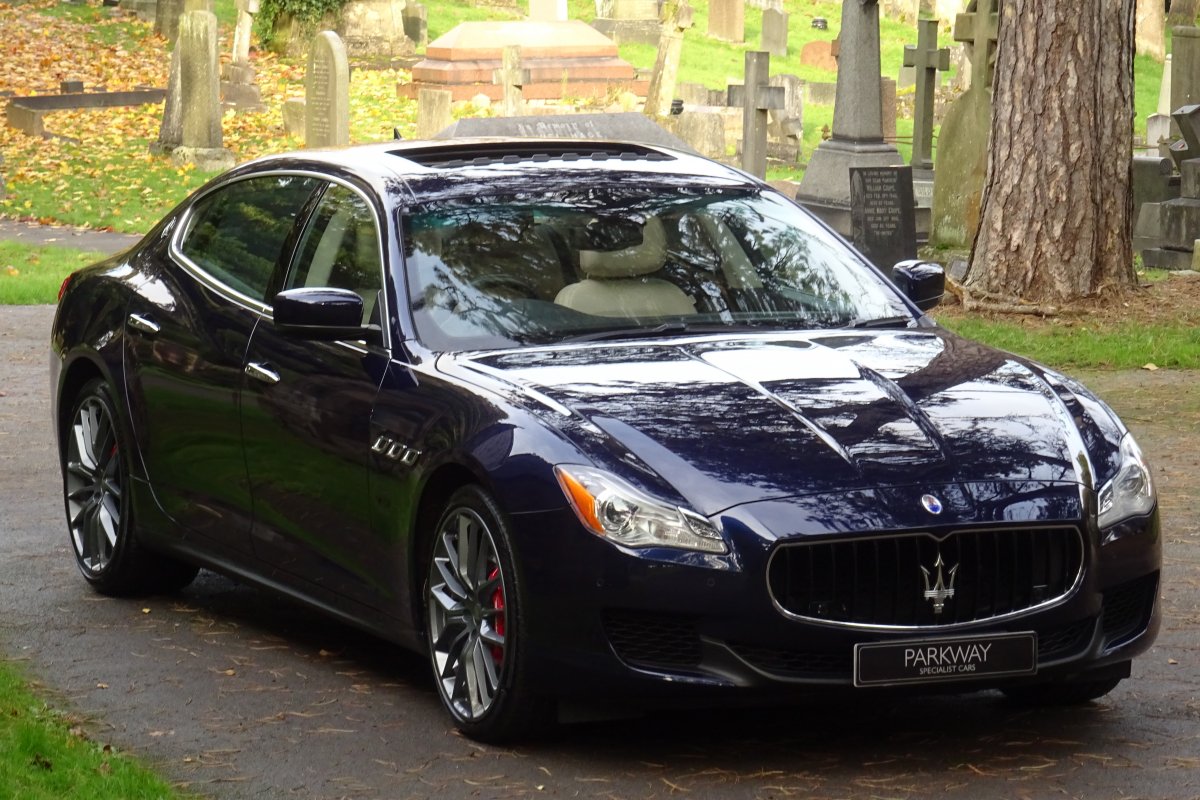
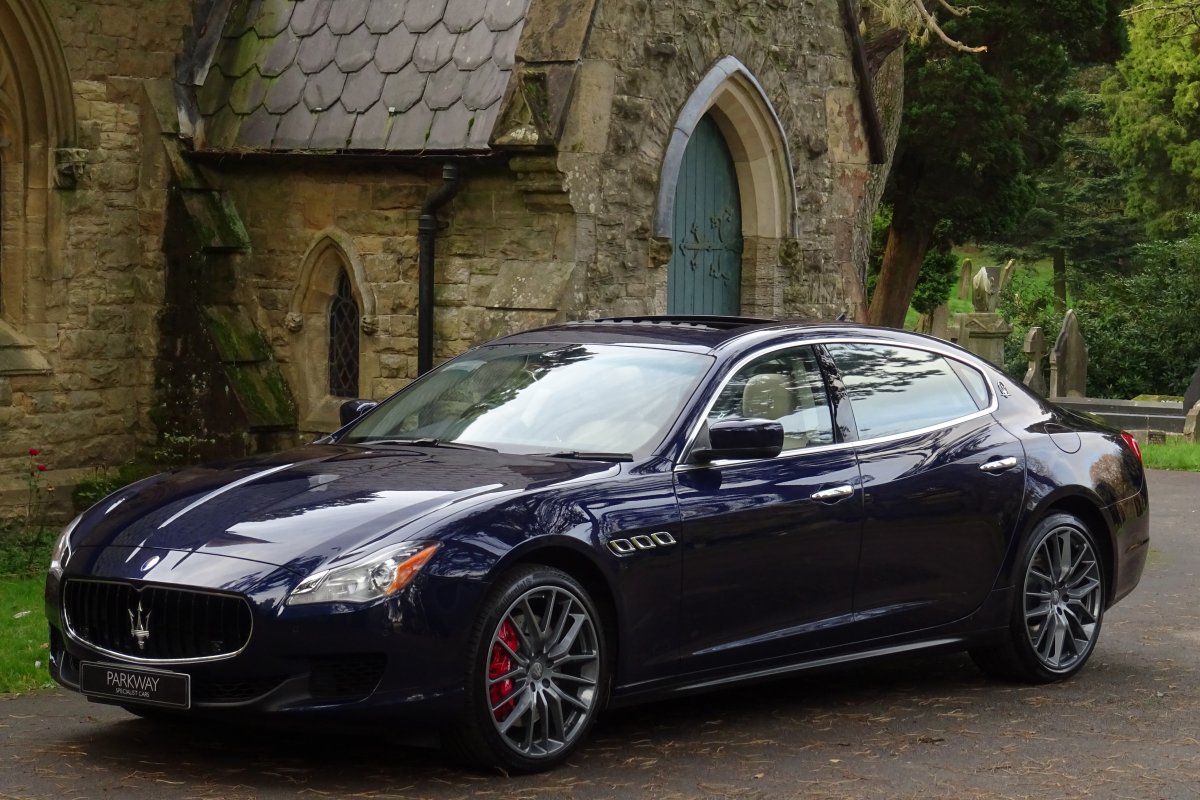
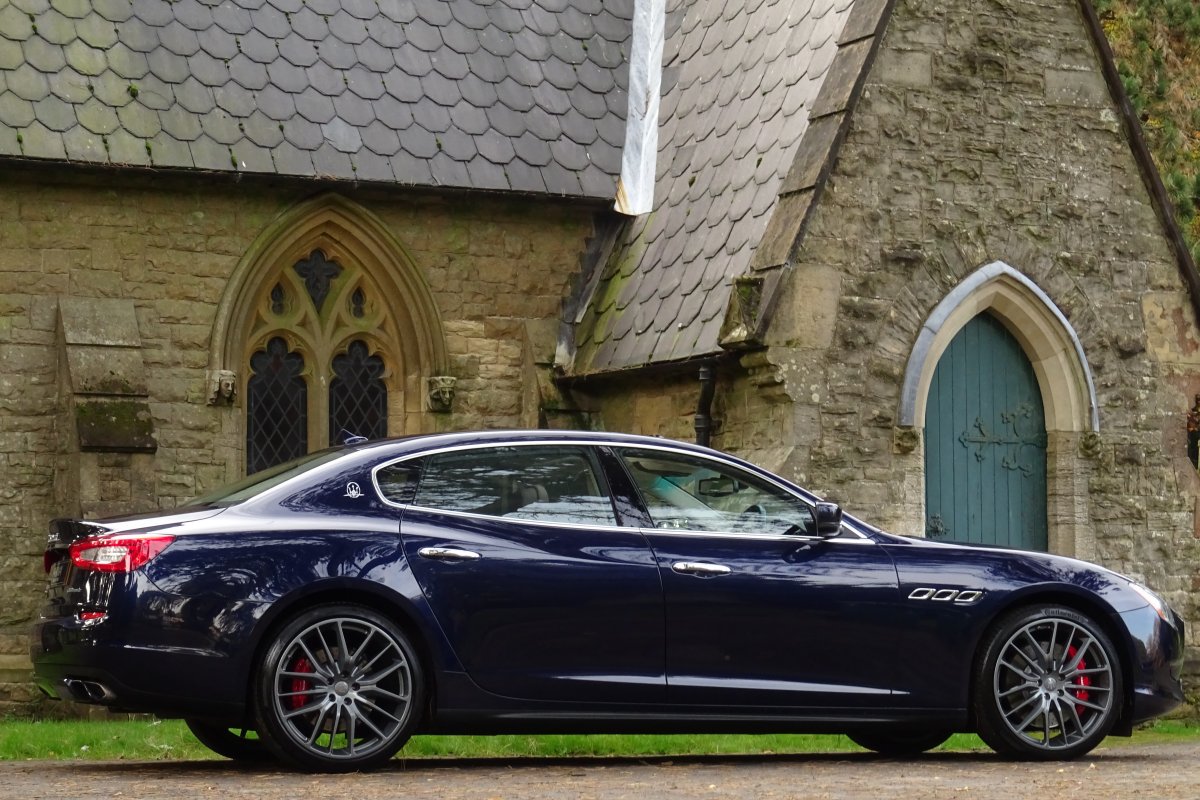
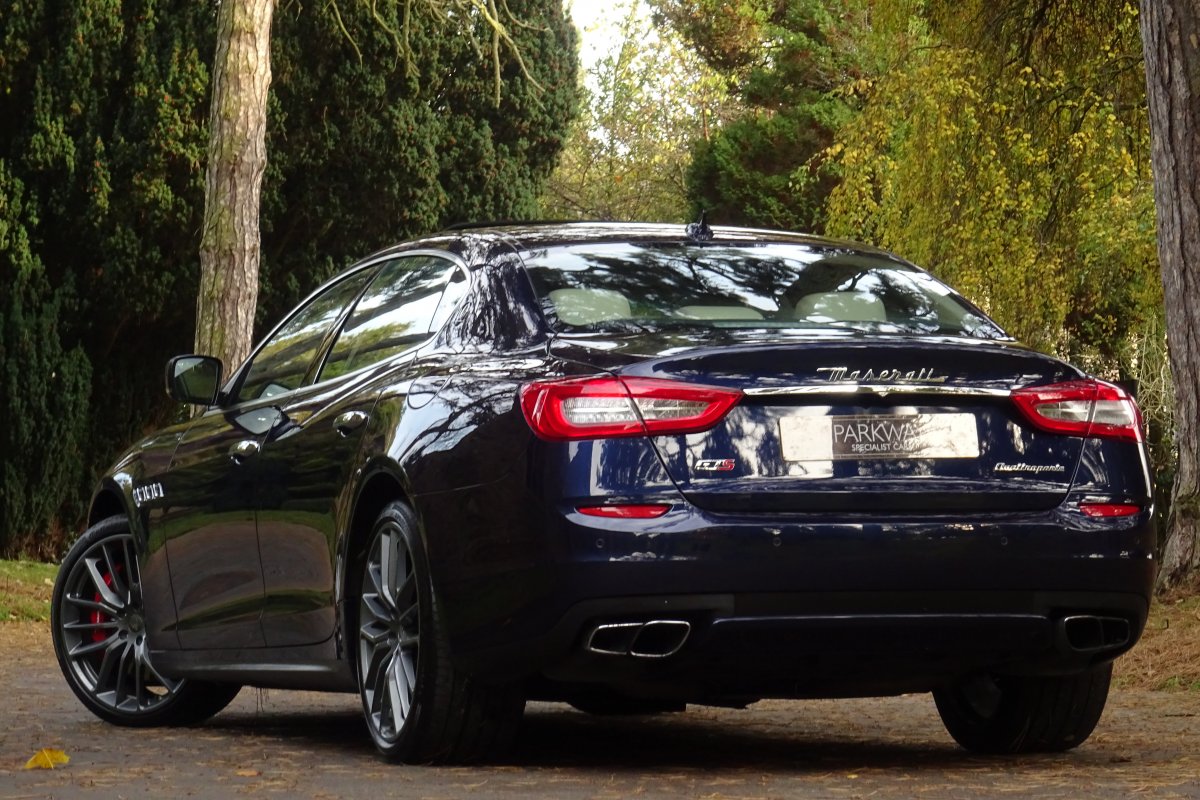
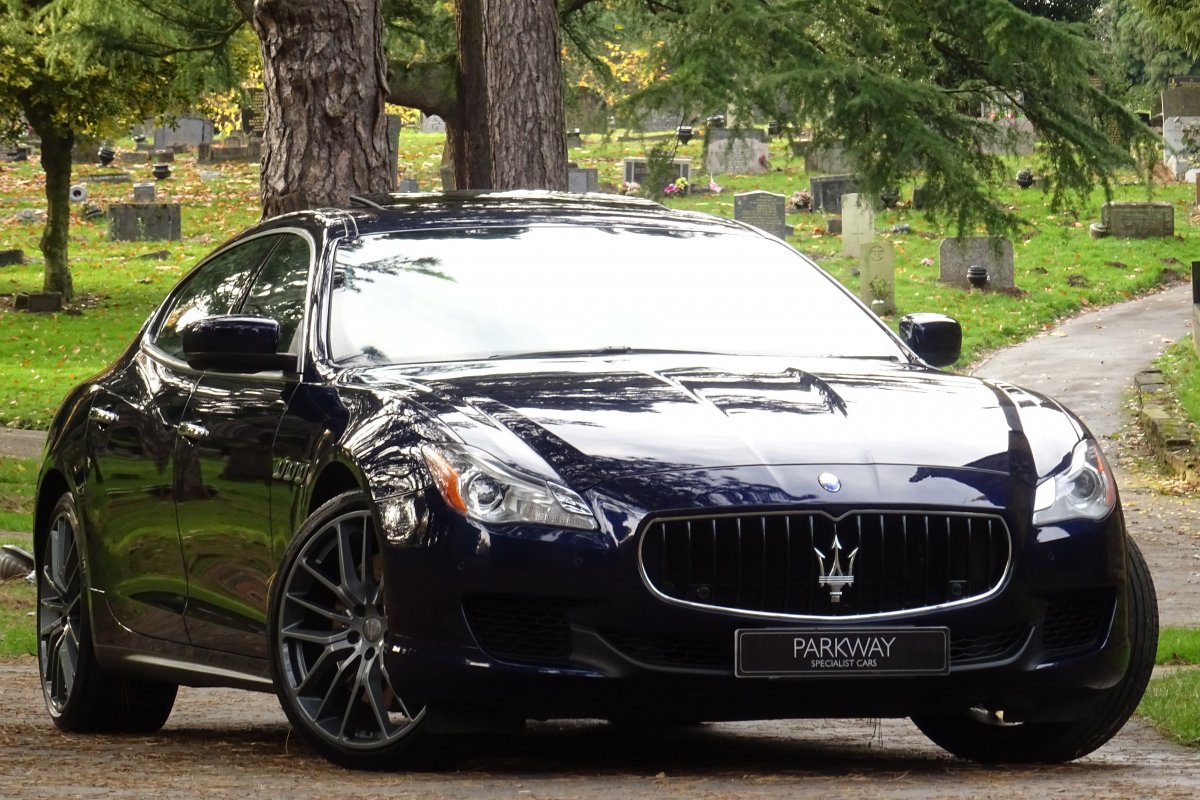
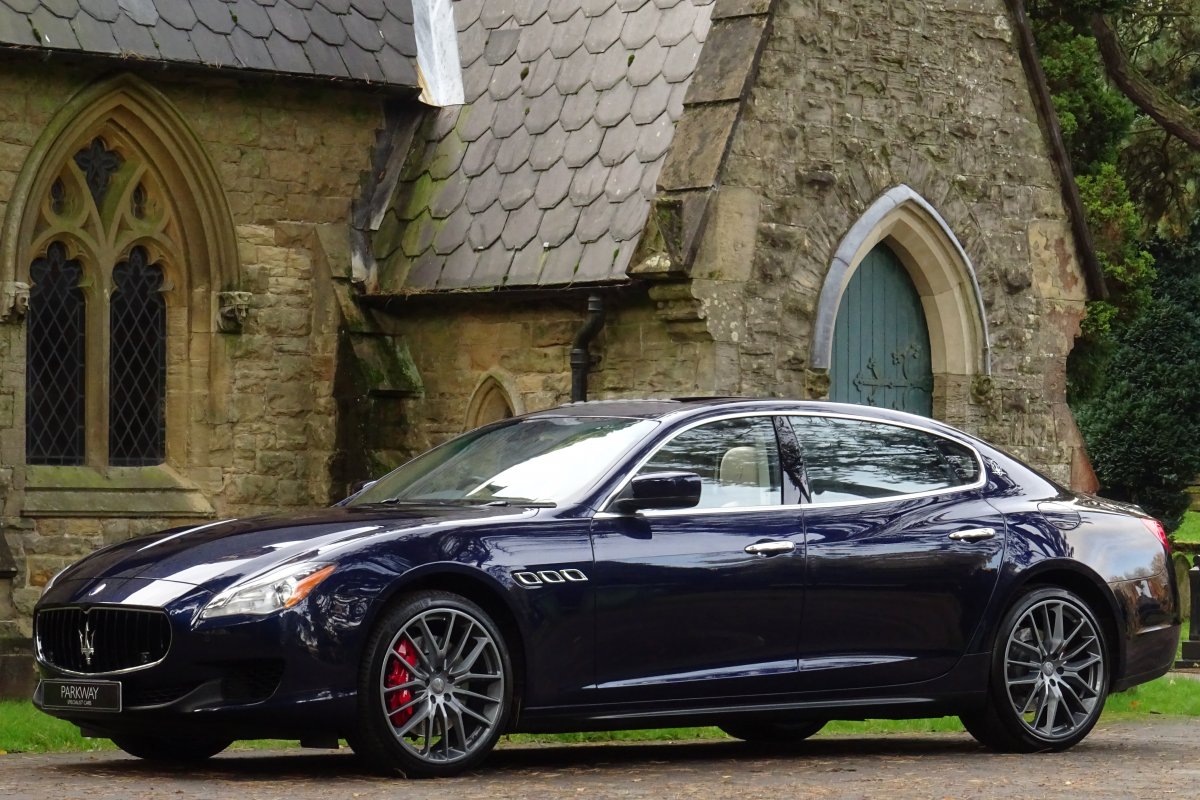
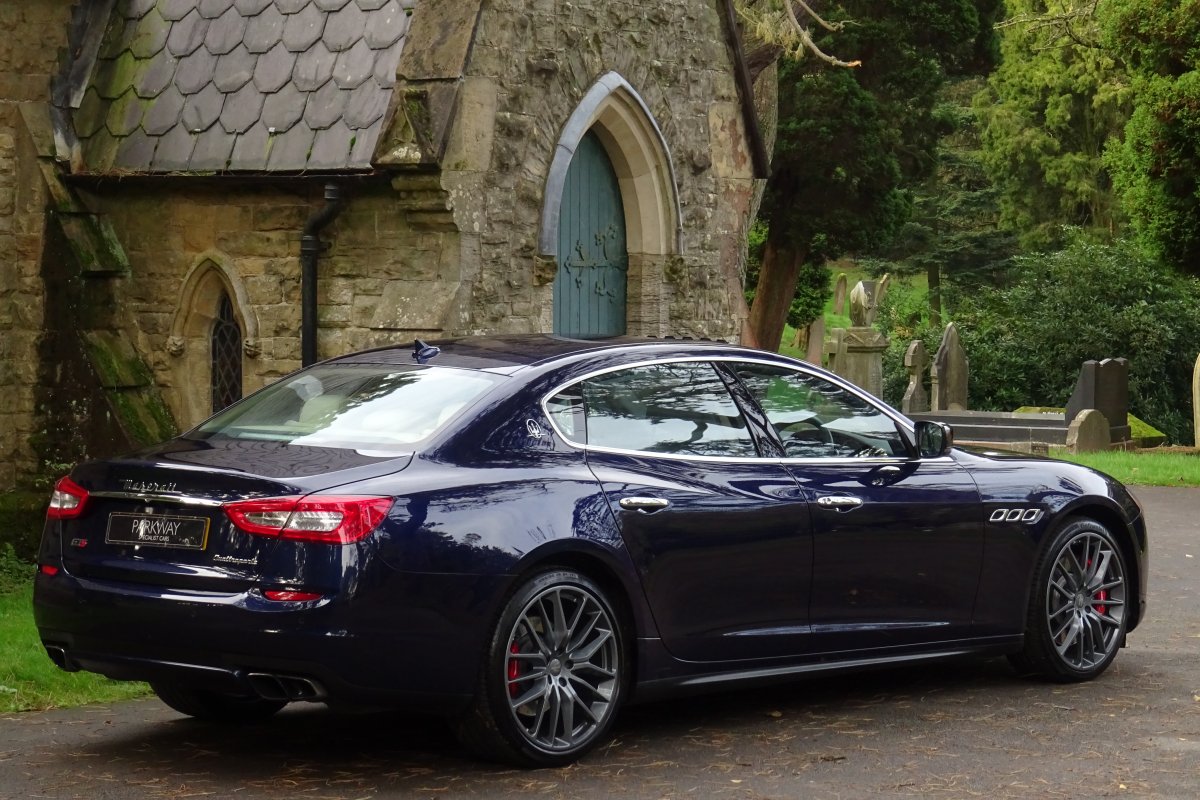
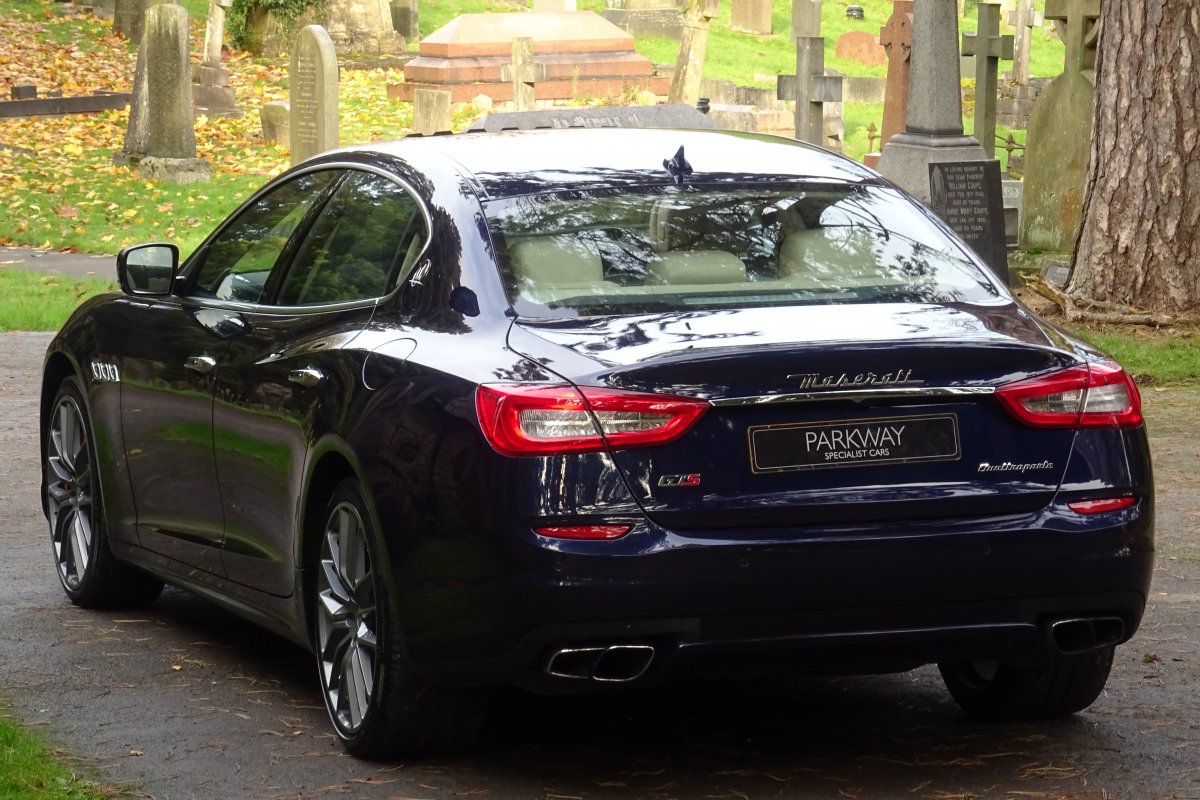
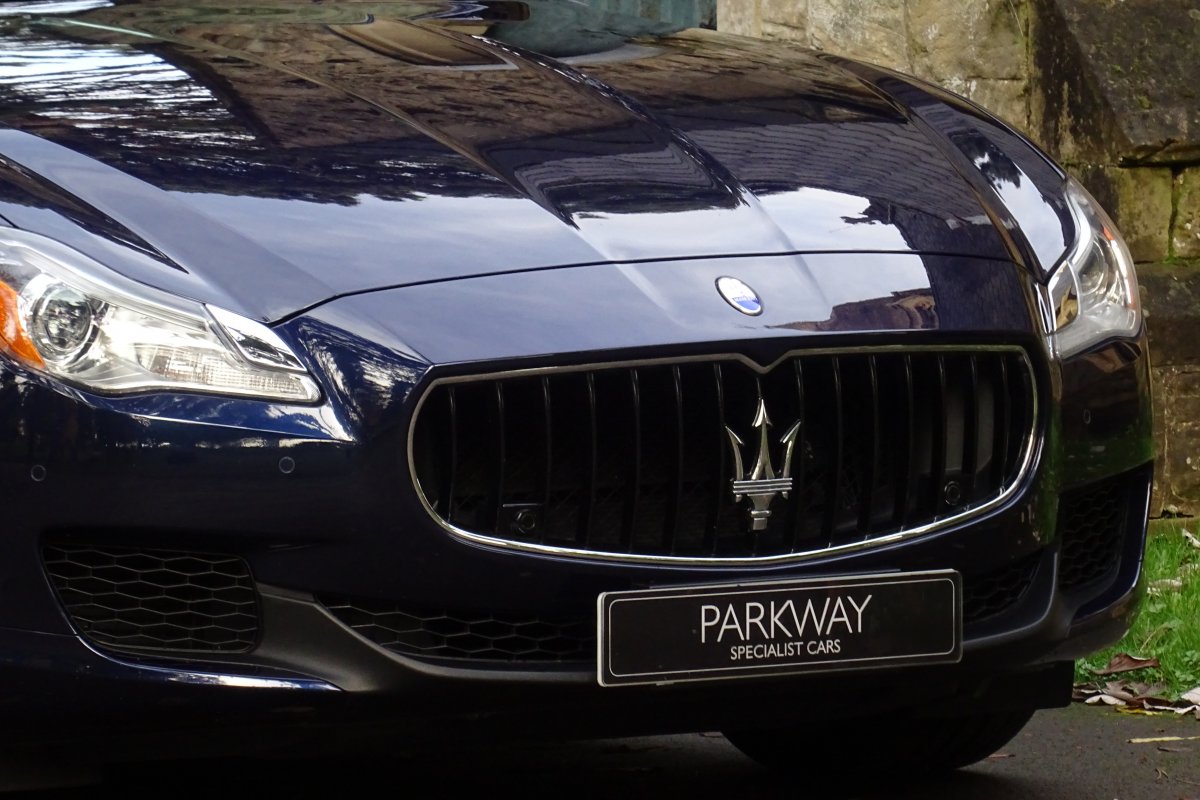
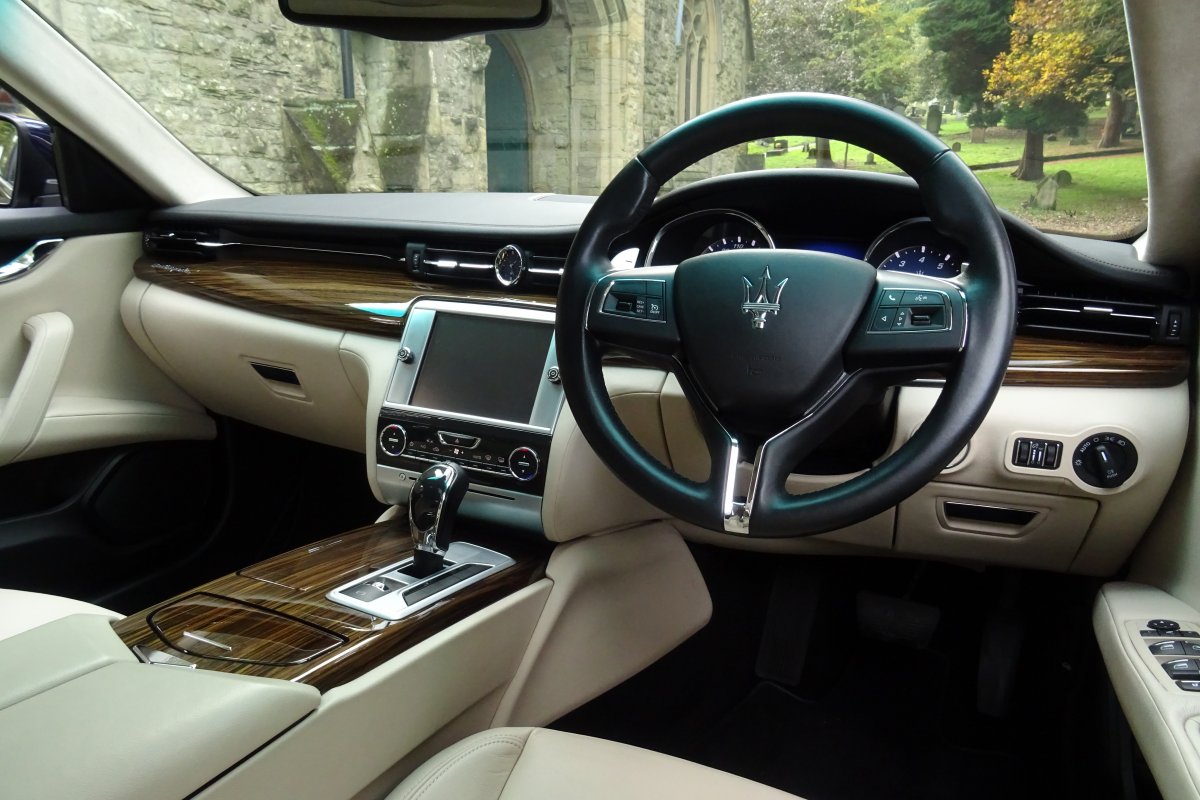
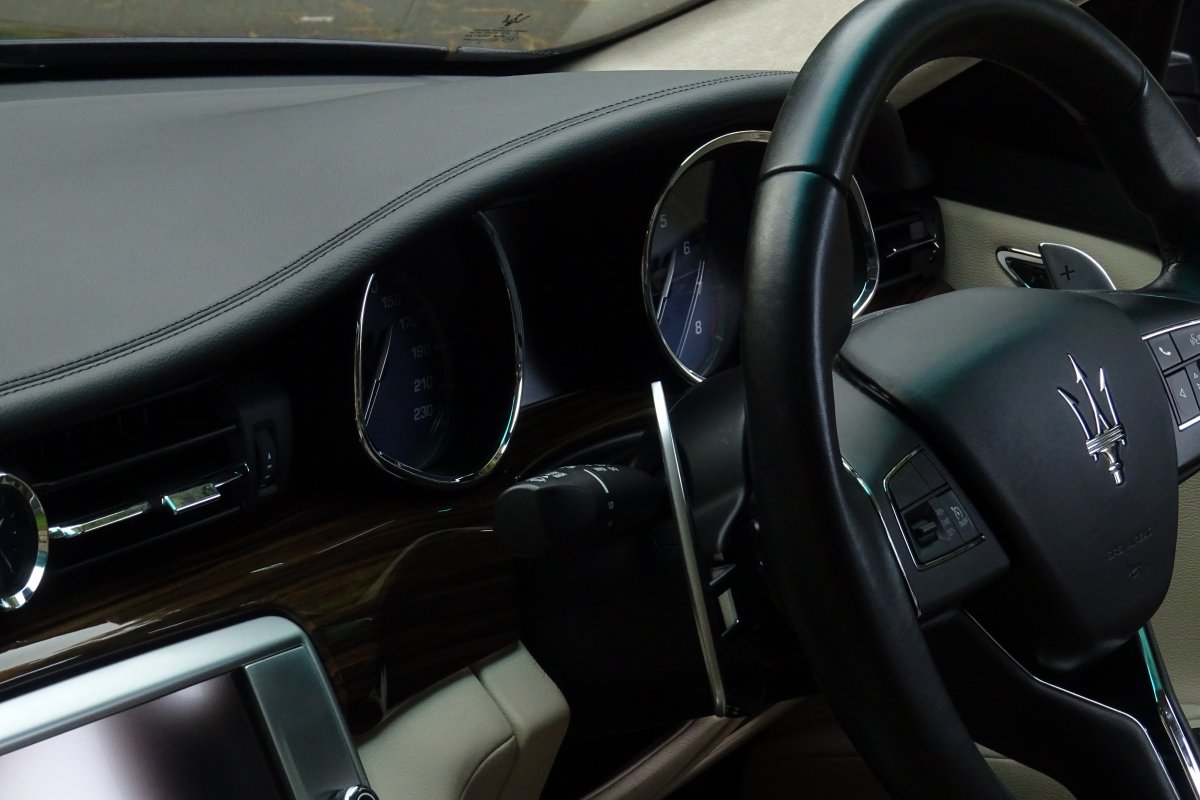
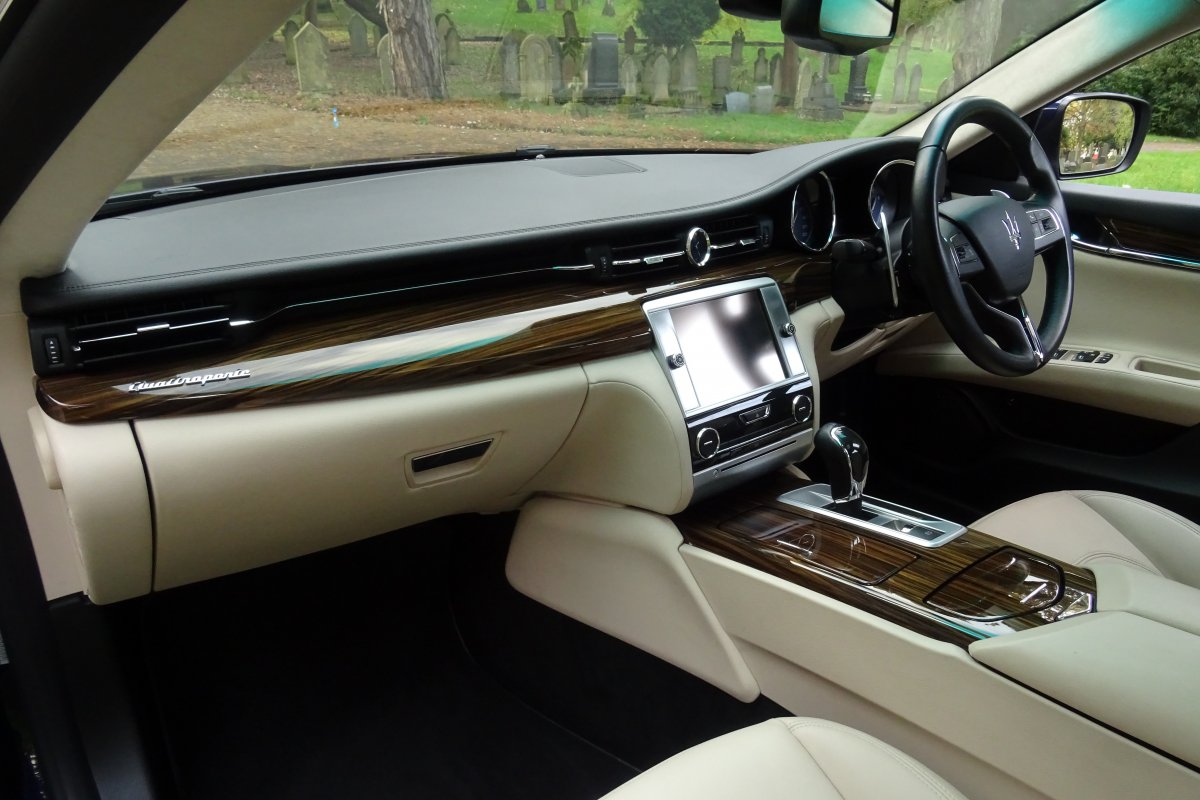
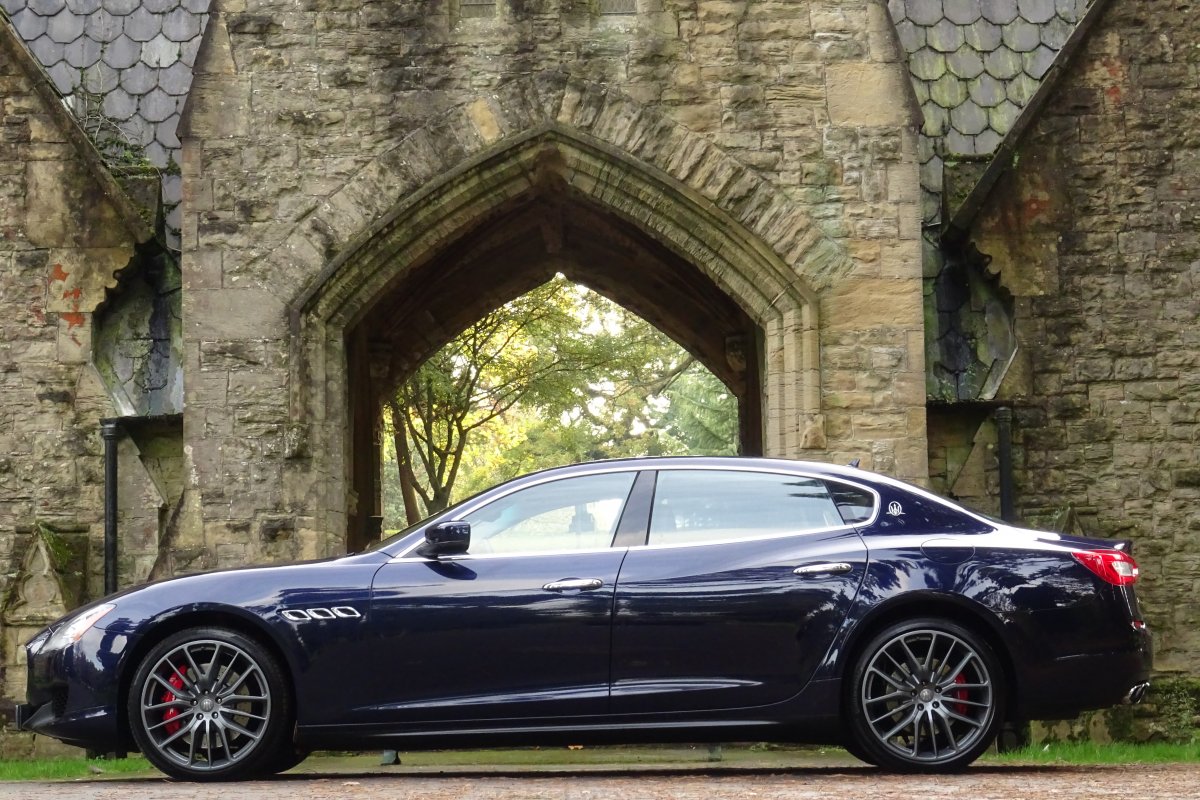
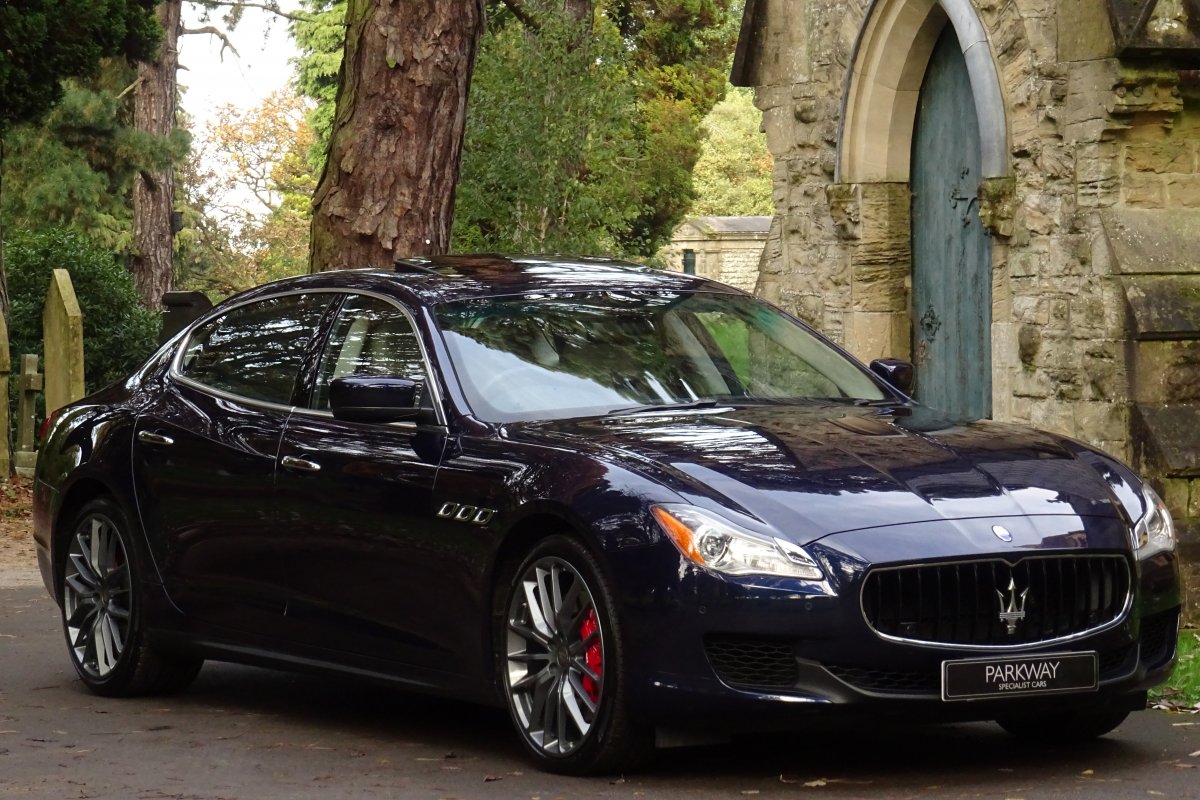
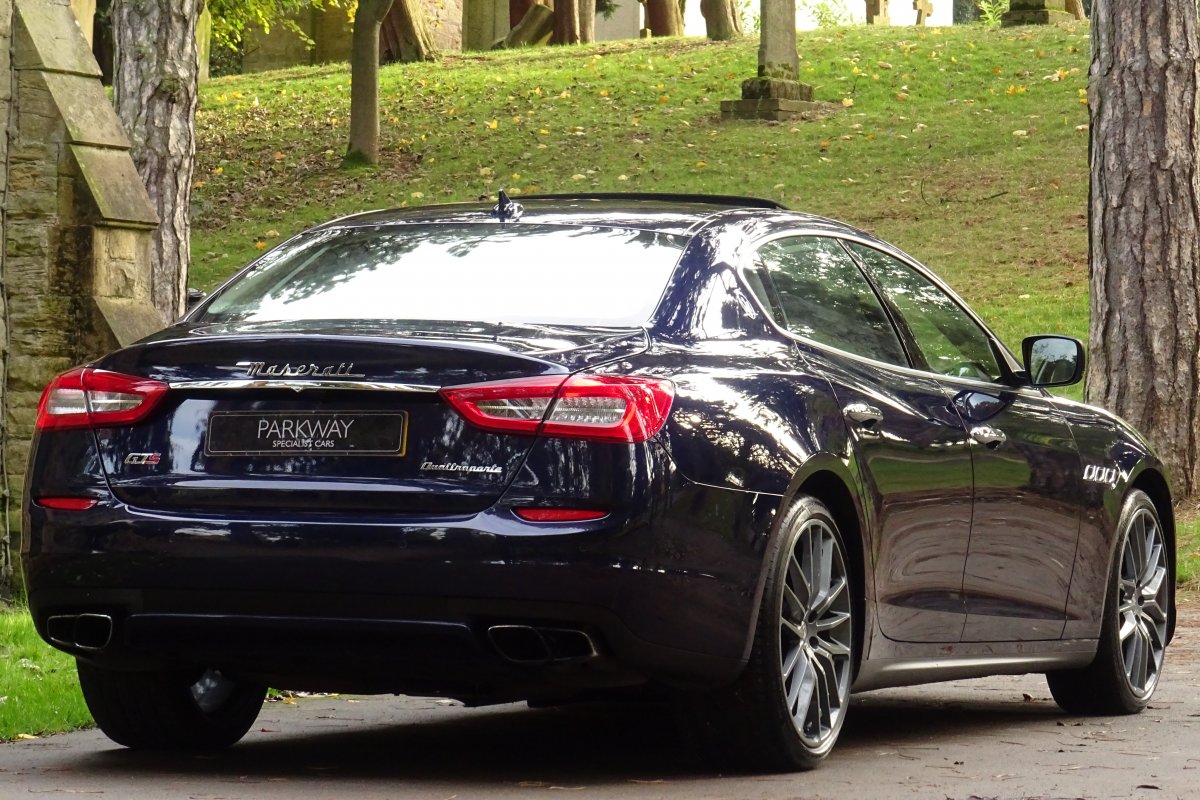
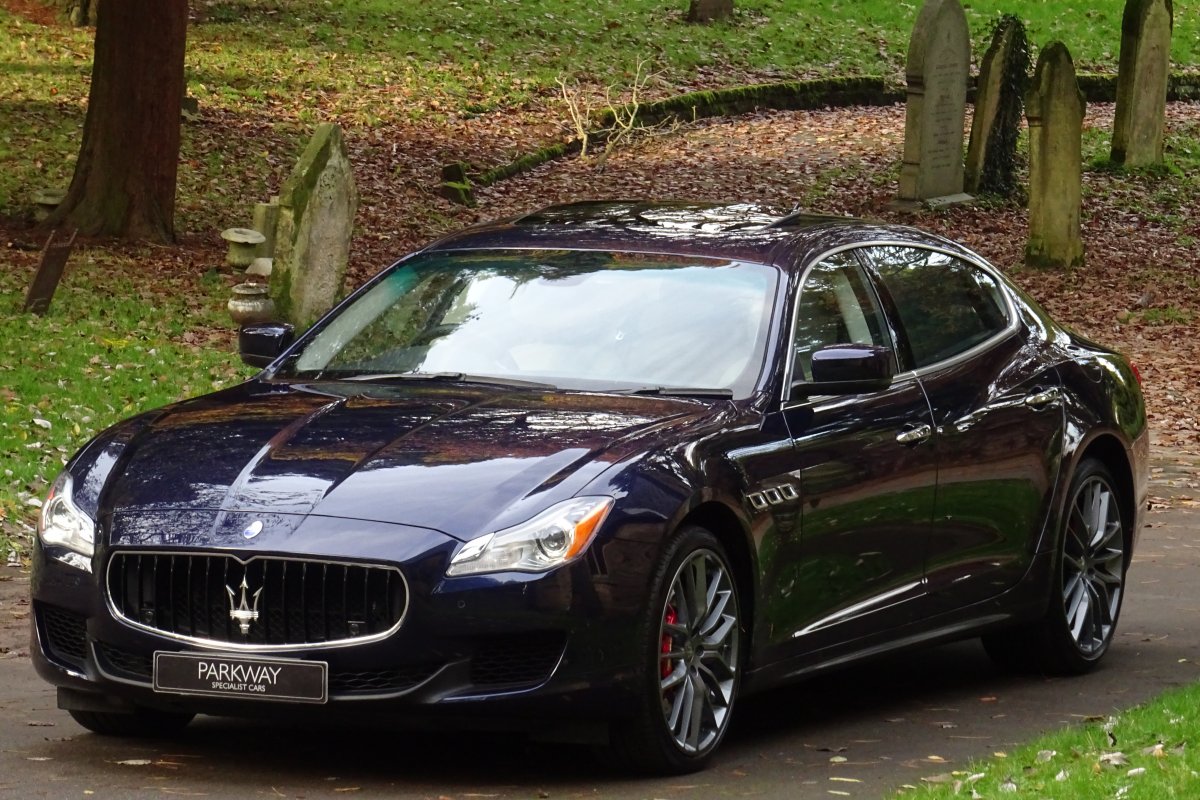
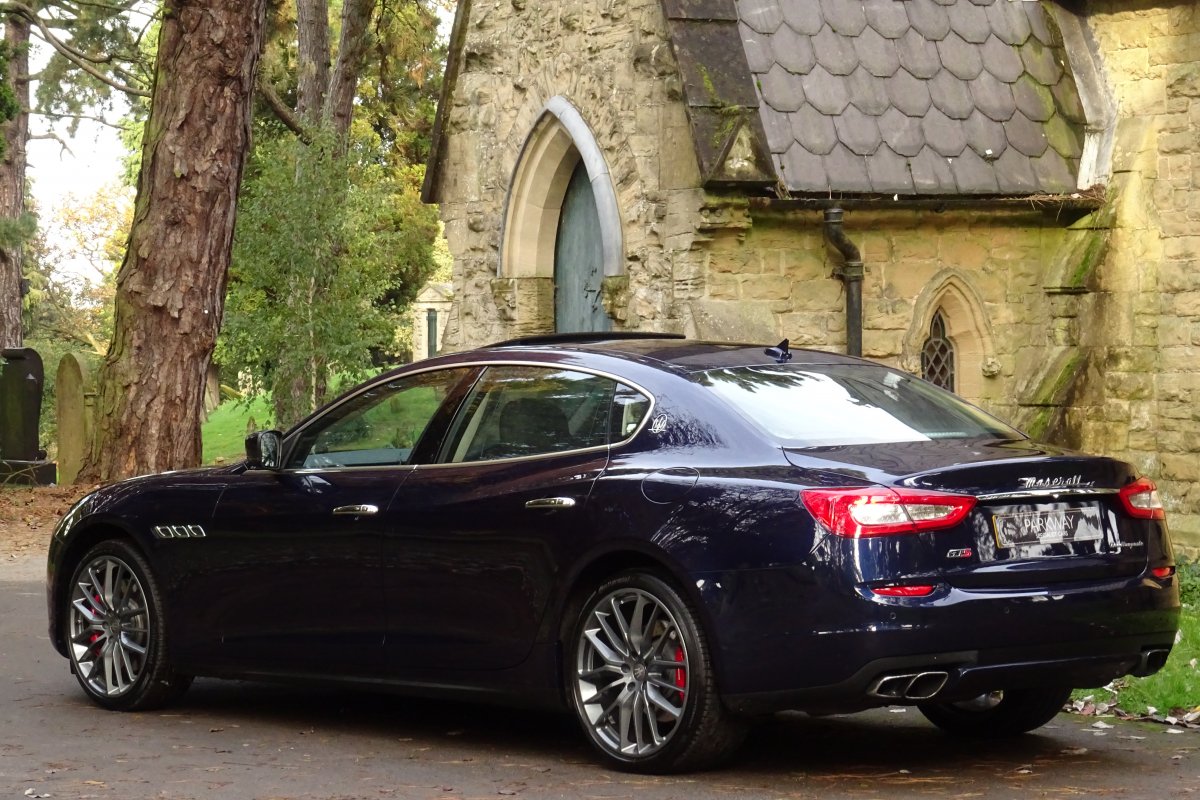
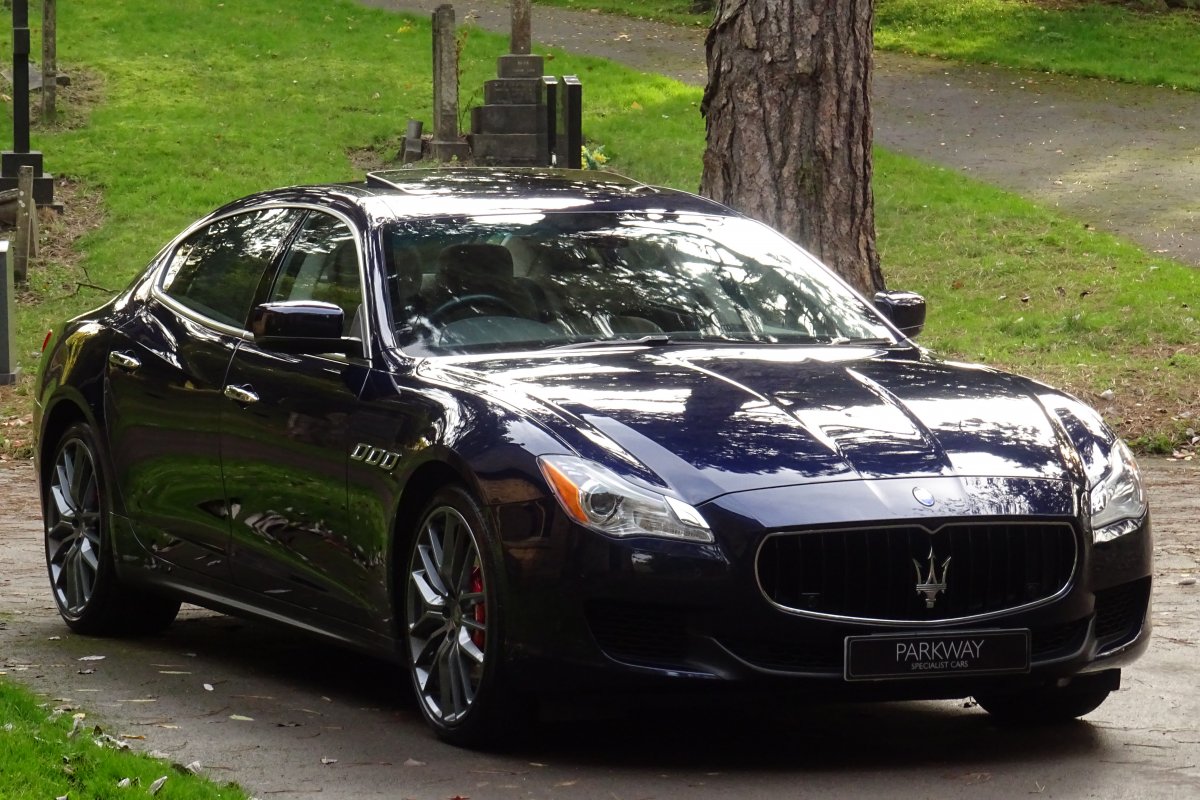
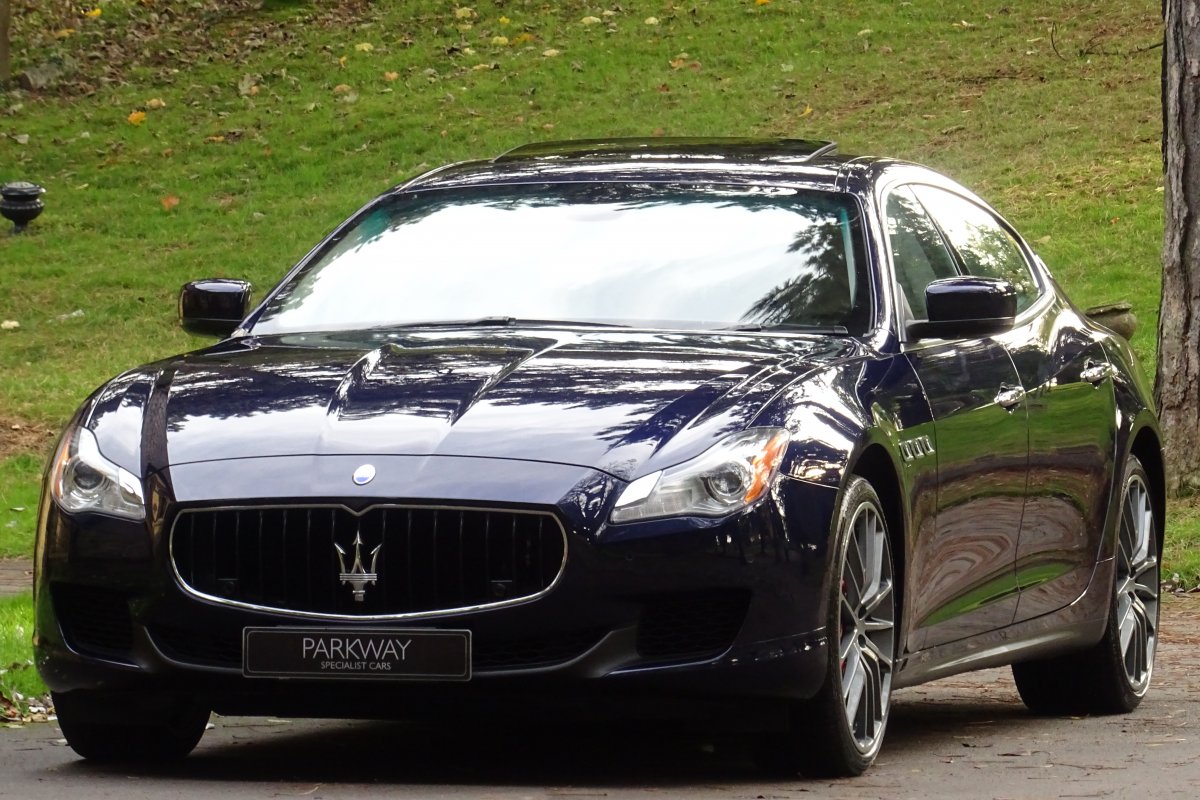
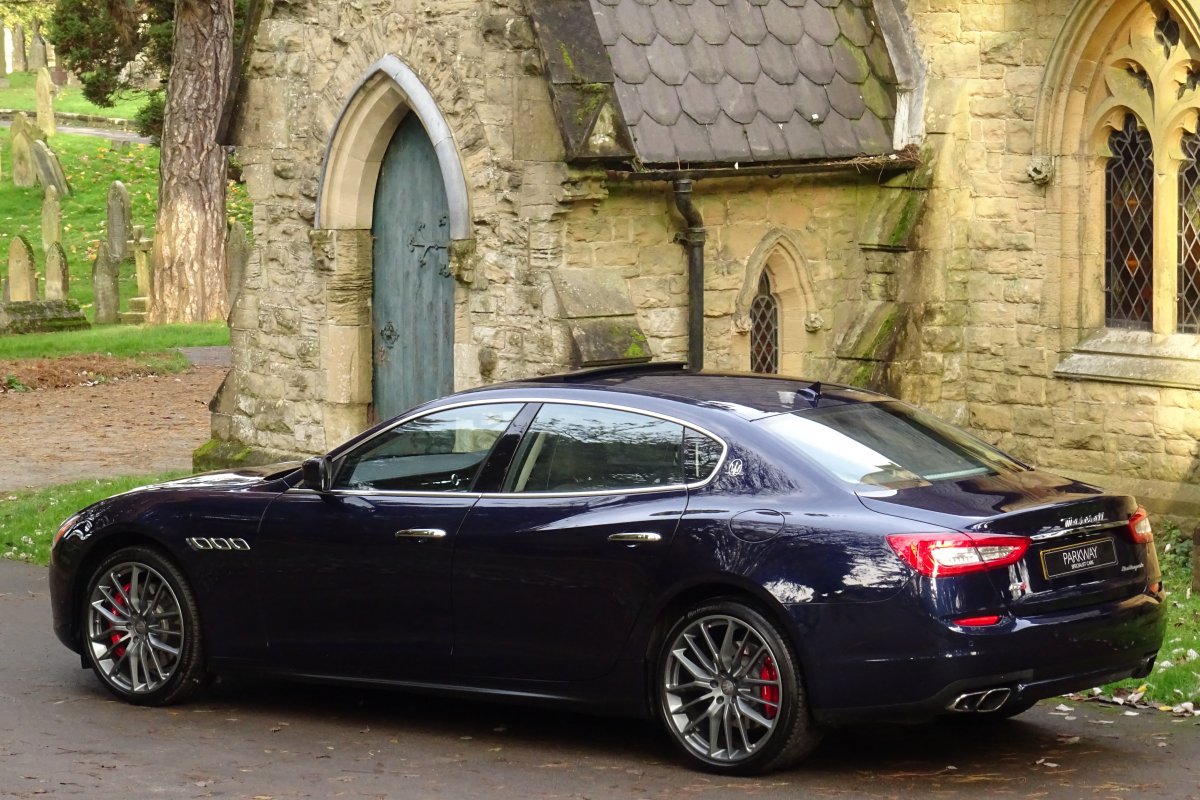
The new Quattroporte was designed at a special Maserati-only department within the Fiat Group Centro Stile design centre, under the guidance of ex-Pininfarina designer Lorenzo Ramaciotti. Drivetrains, platform, suspension, and body elements such as the front doors are common to the Quattroporte and the smaller Ghibli saloon, which sits on a 6.8 inch shorter wheelbase. The Quattroporte is manufactured at the Officine Maserati Grugliasco plant in Grugliasco, near Turin, dedicated to Giovanni Agnelli; this former Bertone plant was acquired by Fiat in 2009 and renovated for production of the two cars.
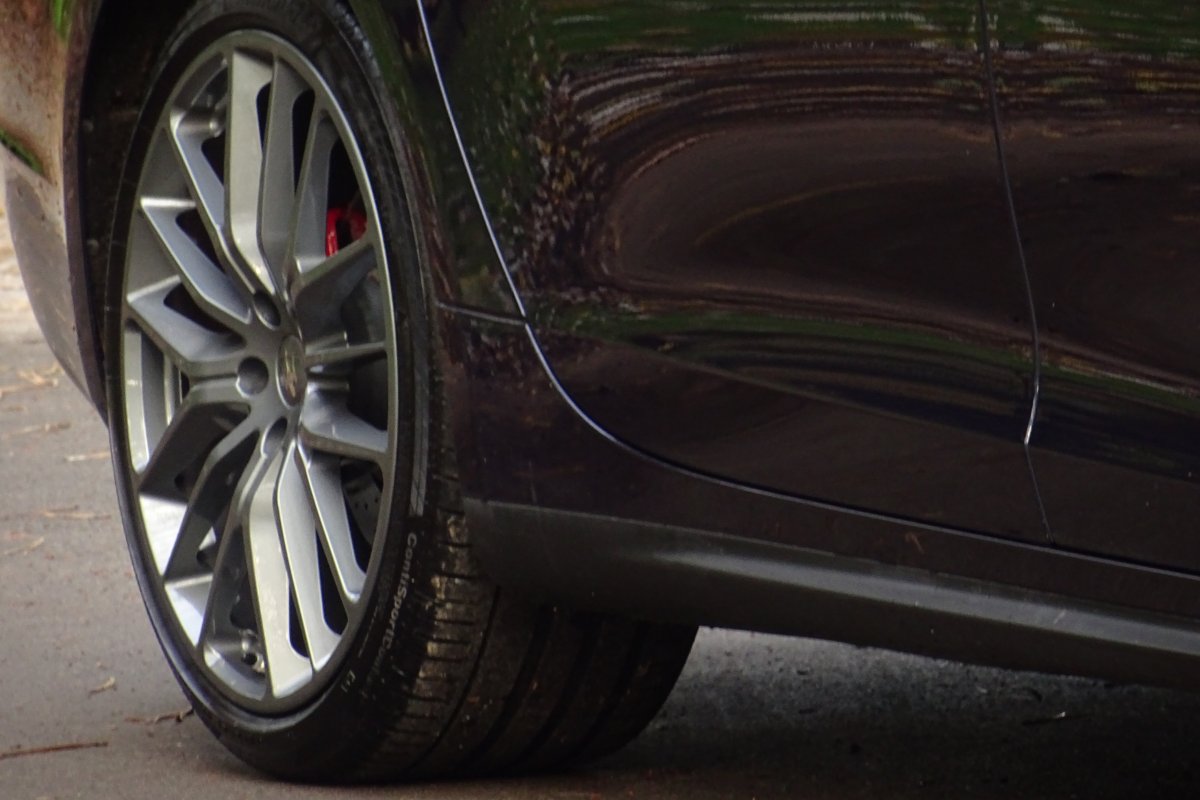
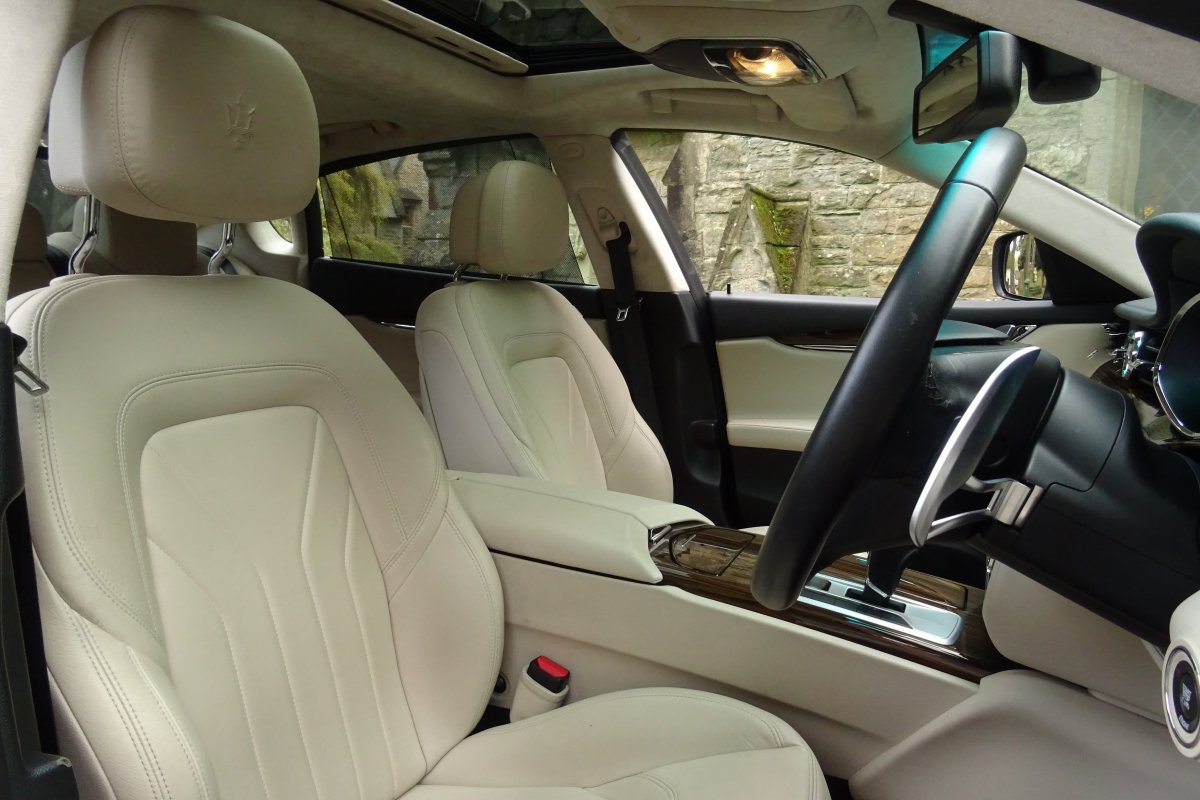
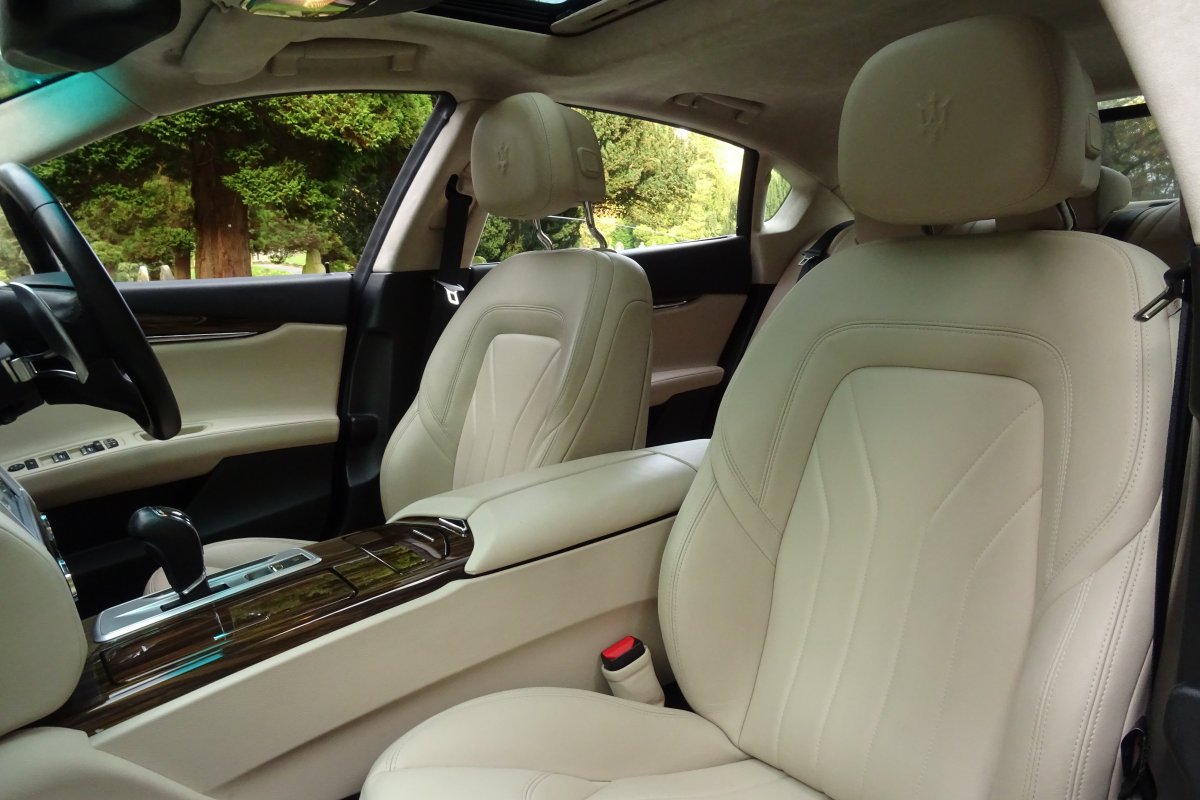
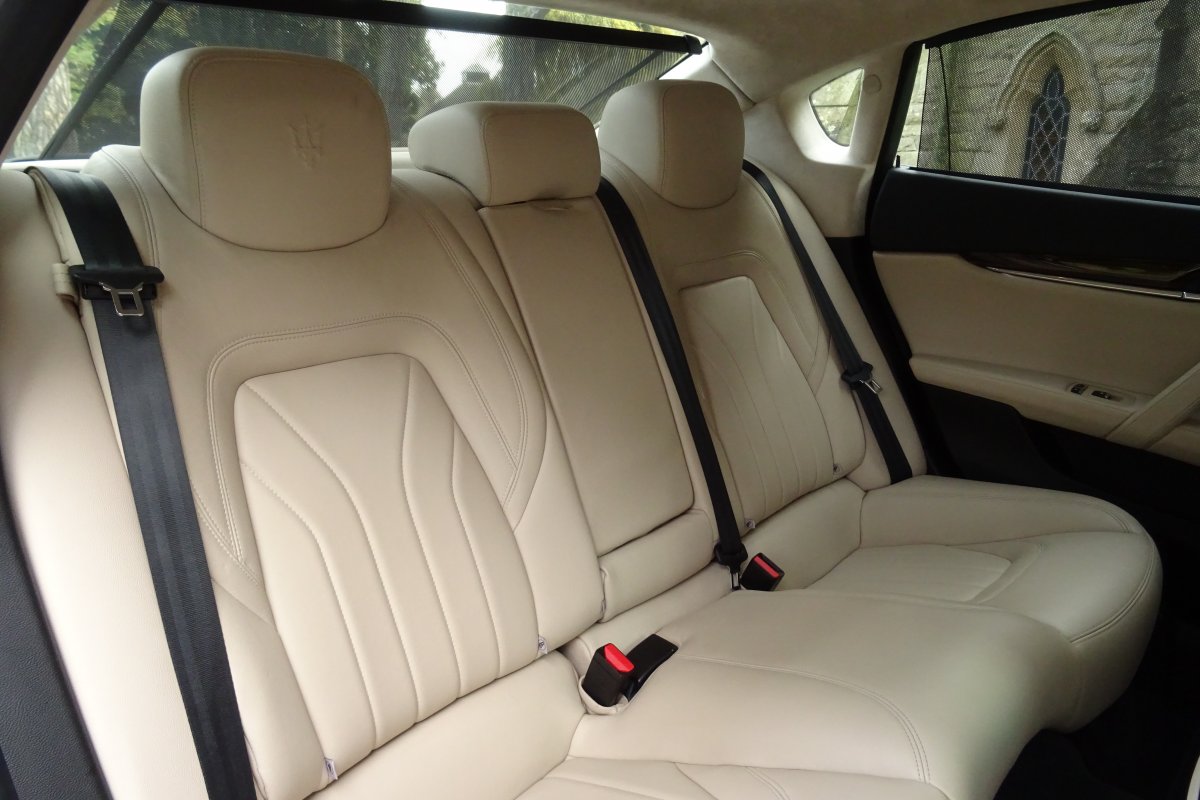
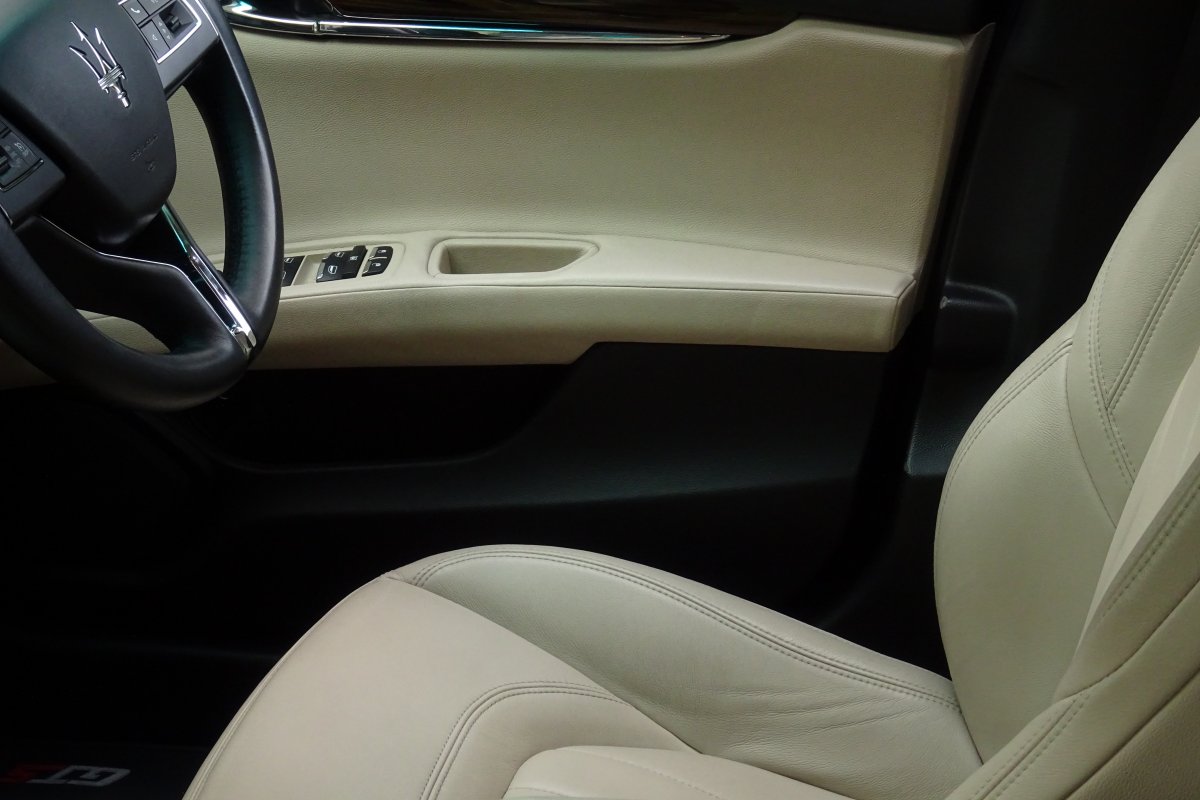
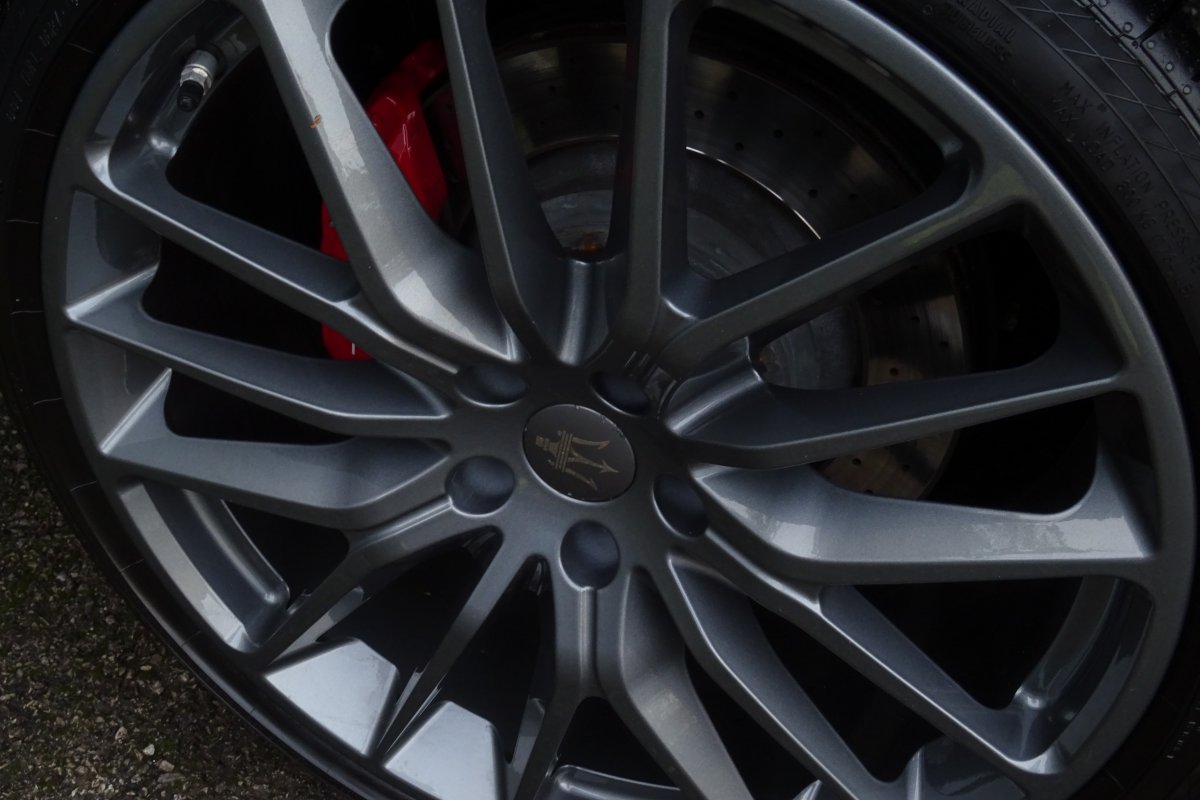
The Quattroporte uses a mixed steel and aluminium unibody chassis. Front and rear crash structures, the shock towers, the front wings, all four doors, the engine bonnet and the boot lid are made of aluminium. Quattroporte has an exceptional drag coefficient of Cd=0.28. Front suspension uses unequal length wishbones with a forged aluminium upright/hub carrier, and an anti-roll bar, rear suspension is a 5-link, with four aluminium links and a larger, steel fifth lower arm that also serves as a spring seat. A front aluminium subframe supports the engine by two mounting points; the steering rack and the lower suspension arms. A rear subframe, made of steel, houses the differential and supports all of the five suspension links. Unlike the predecessors, the new Quattroporte has frameless doors.
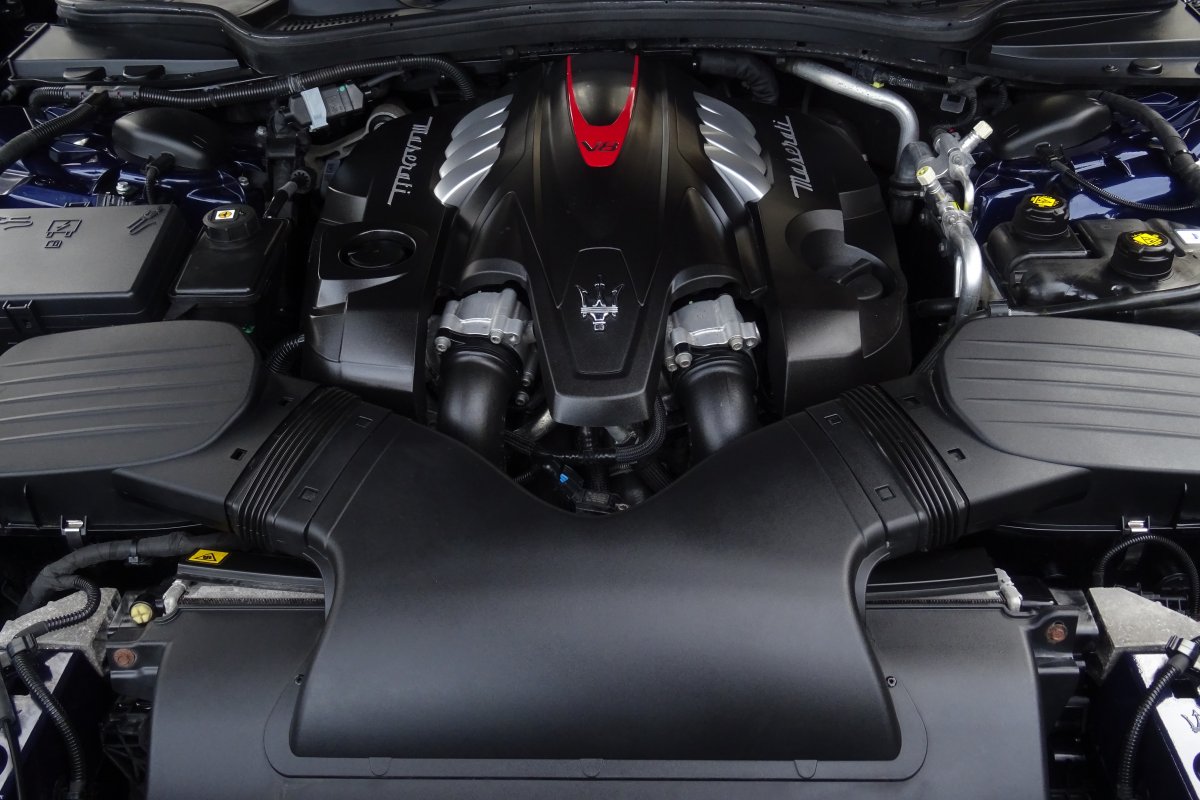
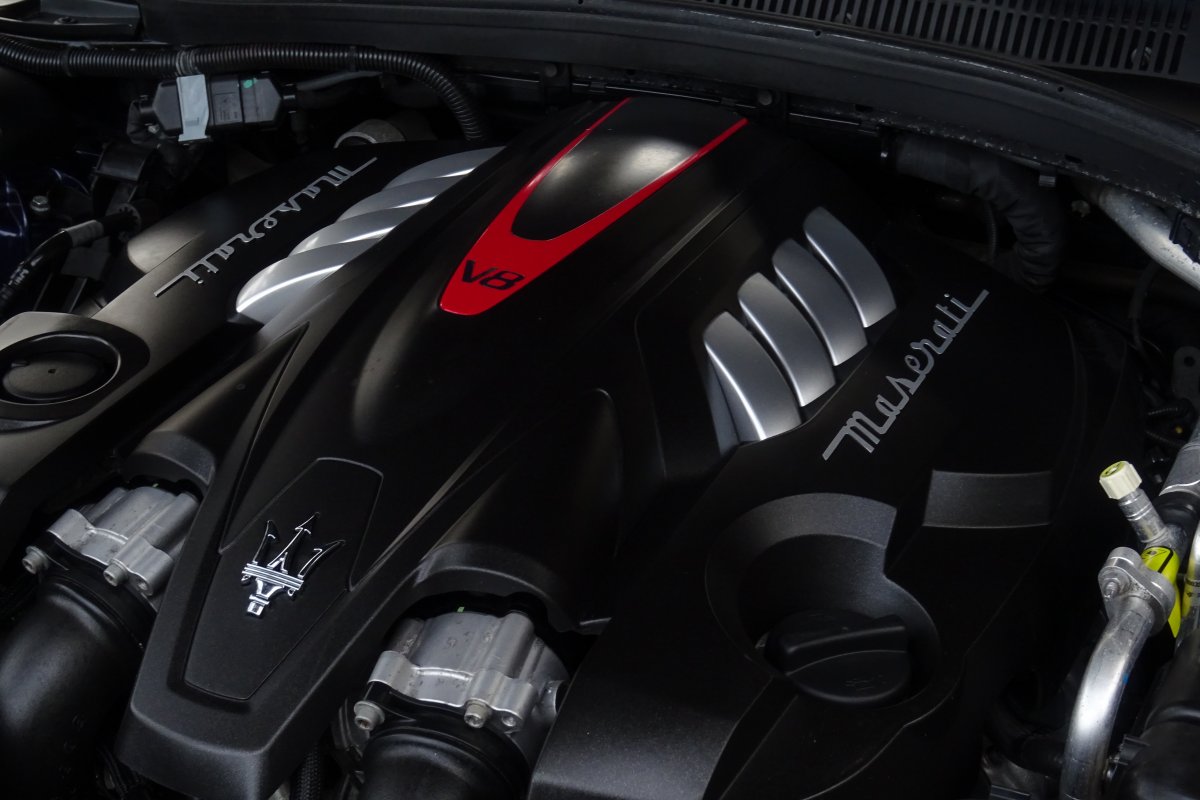
The Quattroporte is offered with range of two petrol engines. The Quattroporte GTS features a variant of the F154 engine platform shared with the Ferrari 488, the Portofino and other Ferrari models. The engine is a 3.8-litre 90° twin-turbocharged V8, generating a maximum power output of 530 bhp.